Shoulder Pain
 At some point in our lives, almost all of us will experience significant shoulder pain. In 2006, 7.5 million people went to their doctor because of shoulder pain. More than half were for rotator cuff problems.
At some point in our lives, almost all of us will experience significant shoulder pain. In 2006, 7.5 million people went to their doctor because of shoulder pain. More than half were for rotator cuff problems.
Shoulder injuries often occur from sports related activities that involve repetitive overhead motions such as tennis, pitching and swimming. Everyday activities like heavy lifting or overhead work can also aggravate the shoulder.
Shoulder problems typically involve the soft tissues such as muscle, tendon or ligament. Most issues can be placed into two major categories, instability or rotator cuff (i.e. impingement).
 Swimmer's Shoulder
Swimmer's Shoulder
Swimmer's shoulder is a type of overuse injury. According to Dr. Scott Koehler and Dr. David Thornson in a 1996 article of The Physician and Sports Medicine, swimmer's shoulder occurs in 38% to 75% of competitive swimmers. The condition is a result of overuse, especially in young swimmers whose skeletons are still developing. Swimmers use a wide range of motion in their rotator cuff. Over time, this motion tends to cause the soft tissue surrounding the space to migrate between the head of the humerus bone and the shoulder blade. You should rest until symptoms abate and learn to use techniques that limit impingement of the shoulder during swim exercises. If your child has swimmer's shoulder, he or she should see a pediatric orthopedic physician.
Dislocated Shoulder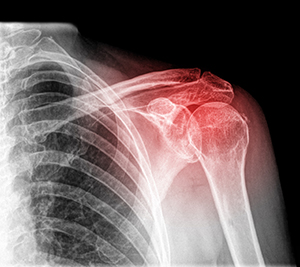
If you have a dislocated shoulder, it can either be partially dislocated or fully dislocated. This can happen from falling or from contact sports like rugby or football. A hard hit pulls the arm out of the shoulder socket. It will swell up, become numb and weak, and bruise. A doctor will pop it back into place and then follow up orthopaedic care will be necessary until it regains stability.
Shoulder Separation
The AAOS reports that football players often sustain a shoulder separation. However, any person who falls on the tip can separate his shoulder. Shoulder separation (or AC separation) occurs when the shoulder blade and collar bone work away from one another. A blow or overuse can cause this type of injury. The ligaments aligning the joint may be stretched or torn. Your orthopedic physician may prescribe a sling, ice, rest and medication. If the clavicle and shoulder blade are completely separated, surgery may be necessary.
Brown Professor

Full Professor leading the way with clinical and basic science research of the latest advances in orthopedic surgery and injury prevention and teaching new physicians.
Board-Certified Surgeon

Chief of Sports Medicine and Sports Medicine Fellowship Director: Department of Orthopedic Surgery. Board Certified in Orthopedic Surgery and Orthopedic Sports Medicine.
Sport Team Physician

Dr. Fadale is currently the head physician for Brown University Athletics and the Providence Bruins Professional Hockey Team (AHL).
Need an Appointment?
We have made it easier to schedule appointments, click the button to fill out an online appointment request form through the University Orthopedics scheduling portal or call the new central scheduling line 401-457-1500 to schedule an appointment.
